About the efficiency of nanoscintillators for photodynamic therapy

Anne-Laure Bulin, Andrey Belsky, David Amans, Gilles Ledoux and Christophe Dujardin (team Luminescence), in collaboration with colleagues from the Moscow State University, have published a paper entitled « Modelling energy deposition in nanoscintillators to predict the efficiency of the X-ray-induced photodynamic effect » in the journal Nanoscale.
|
|
Scintillating nanoparticles (NPs) in combination with X- or γ-radiation have a great potential for deep-tissue cancer therapy because they can be used to generate singlet oxygen in tumours by means of the photodynamic effect (see this iLM news). |
|
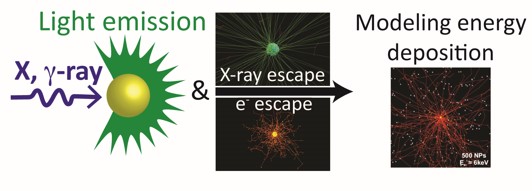
To understand the complex spatial distribution of energy deposition in a macroscopic volume of water loaded with nanoscintillators, we have developed a GEANT4-based Monte Carlo program. We thus obtain estimates of the maximum expected efficiency of singlet oxygen production for various materials, X-ray energies, NP concentrations and NP sizes. A new parameter, η_nano, is introduced to quantify the fraction of energy that is deposited in the NPs themselves, which is crucial for the efficiency of singlet oxygen production but has not been taken into account adequately so far. We furthermore point out the substantial contribution of primary interactions taking place in water, particularly under irradiation with high energy photons. The interplay of all these contributions to the photodynamic effect has to be taken into account in order to optimize nanoscintillators for therapeutic applications. |
|
27/02/2015