Nanotubes déformés pour plastiques conducteurs
Sylvie Le Floch, Christophe Adessi, Alfonso San-Miguel, (team Energie) and Nicholas Blanchard (instrumentation), in collaboration with colleagues from Bordeaux (France), Saclay (France), Zaragoza (Spain), Jena (Germany) and Halle (Germany), have published an article entitled «Radial collapse of carbon nanotubes for conductivity optimized polymer composites» in the journal Carbon.
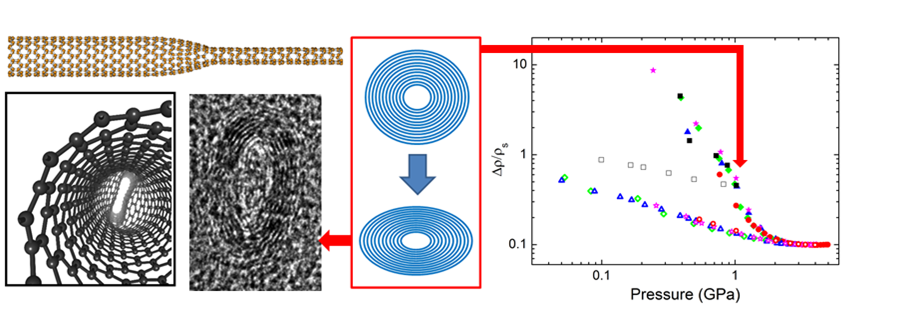 Adding a small quantity of carbon nanotubes to electrically insulating polymers gives them a metallic character. These composite materials – mechanically reinforced conductive plastics – start to find applications in various domains such as antistatic films or paints or in sensor development. Combining modelling and experiments on industrial samples we have shown that a compression in the Gigapascal domain (10,000 atmospheres) results in a considerable improvement of the composite’s electrical conductivity. We have also shown that the dominant mechanism involved in this process is the radial deformation of the carbon nanotubes. This work, for which the first electron microscopy images of pressure deformed carbon nanotubes were obtained, opens a new path for optimizing conductive plastics.
Adding a small quantity of carbon nanotubes to electrically insulating polymers gives them a metallic character. These composite materials – mechanically reinforced conductive plastics – start to find applications in various domains such as antistatic films or paints or in sensor development. Combining modelling and experiments on industrial samples we have shown that a compression in the Gigapascal domain (10,000 atmospheres) results in a considerable improvement of the composite’s electrical conductivity. We have also shown that the dominant mechanism involved in this process is the radial deformation of the carbon nanotubes. This work, for which the first electron microscopy images of pressure deformed carbon nanotubes were obtained, opens a new path for optimizing conductive plastics.