Angle mort en conduction de la chaleur
Ali Alkurdi, Samy Merabia (équipe Modélisation de la Matière Condensée et Interfaces) et Stéphane Pailhès ( (équipe (nano)matériaux pour l’énergie ), ont publié un article intitulé "Critical angle for phonon scattering: results from ab-initio lattice dynamics calculations" dans la revue Applied Physics Letters.

Critical angle for heat flux at interfaces
Ali Alkurdi, Samy Merabia (team Modelisation of Condensed Matter and Interfaces) et Stéphane Pailhès ( (team NanoMaterials for Energy ), have published an article entitled "Critical angle for phonon scattering: results from ab-initio lattice dynamics calculations" in Applied Physics Letters .
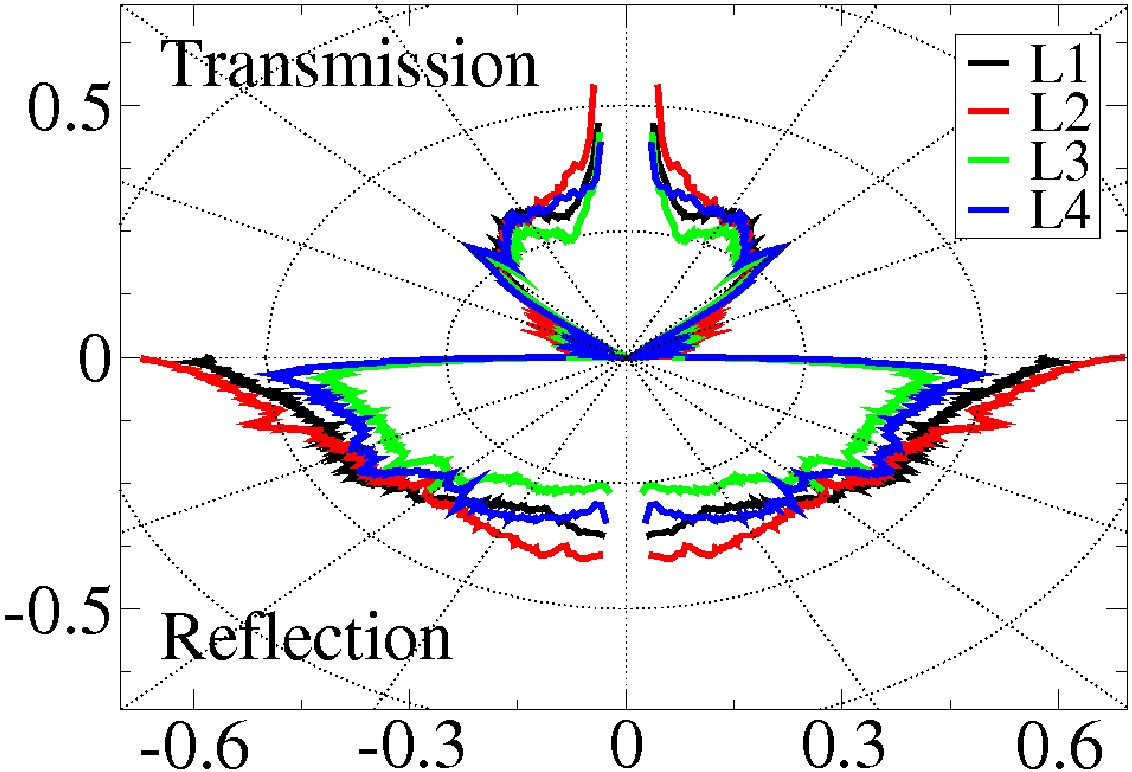
Du fait de la miniaturisation constante des composants microélectroniques, il devient important de comprendre comment évacuer la chaleur à travers des surfaces nanométriques. A ces échelles, le transfert de chaleur entre deux milieux est contrôlé par la transmission des phonons aux interfaces. Les chercheurs de l'ILM ont développé une méthode innovante qui combine dynamique de réseau et calculs ab initio afin de calculer la transmission des phonons en fonction de leur fréquence et de leur vecteur d'onde. Pour la première fois, les auteurs ont pu caractériser la distribution angulaire du flux de chaleur transmis à l'interface entre deux milieux. Il apparaît qu'il existe un angle critique, typiquement 60 degrés pour des interfaces Silicium/Germanium, au delà duquel la transmission de la chaleur est quasiment nulle. Ce résultat permet d'envisager de réaliser des filtres de chaleur en jouant sur l'orientation des interfaces.
Due to the continuous miniaturization of the components of microelectronic devices, it becomes crucial to understand how to evacuate heat across nanoscale interfaces. At these scales, heat transfer between two media is controlled by phonon transmission at interfaces. ILM researchers have developed an innovative method which combines lattice dynamics and ab-initio calculations so as to calculate phonon transmission as a function of both phonon frequency and wavevector. For the first time, the authors could compute the angular distribution of the transmitted heat flux at the interface between two solids. The authors found the existence of a critical angle, typically around 60 degrees for a Silicium/Germanium interface, beyond which heat transmission is negligible. This result could be used to realize phonon filters by playing with the orientation of the interfaces .
19/10/2017