Photonique intégrée libérée des polarisations rectilignes
Stéphan Guy, Bruno Baguenard & Amina Bensalah-Ledoux (equipe MNP), en collaboration avec des collègues de Bejaïa et de Lyon, ont publié un article intitulé "Full polarization control of optical planar waveguides with chiral material" dans la revue ACS Photonics.
Integrated photonics, unlimited by linear polarizations
Stéphan Guy, Bruno Baguenard & Amina Bensalah-Ledoux (team MNP), in collaboration with colleagues from Bejaïa and Lyon, have published an article entitled "Full polarization control of optical planar waveguides with chiral material" in the journal ACS Photonics.
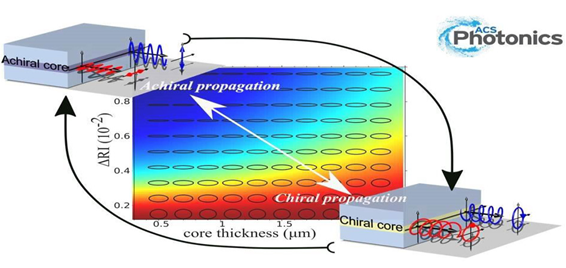
La lumière polarisée elliptiquement ne peut se propager dans des guides d’onde planaires conventionnels. En effet, à cause de leur géométrie, seules les polarisations rectilignes, les fameux TE/TM sont autorisées. Une façon de lever cette restriction est l’utilisation de guides plans « chirOptiques ». Grâce à la chiralité du matériau constituant le cœur de ces guides et à la différence d’indice entre le cœur et la couche de gainage, des modes de polarisations elliptiques voire circulaires peuvent être propagés. Les auteurs ont mis en évidence pour la première fois, la propagation d’ondes de polarisation non linéaire dans des guides d’ondes plans. Le cœur de ces guides d’ondes est constitué d’une couche mince chirale transparente fabriquée à base de silice hybride chirale et possédant un grand pouvoir rotatoire (2◦/mm à 633nm). Par un contrôle du contraste d’indice Δn entre les couches, à 10-3 près, la polarisation des modes propres est modulée de la polarisation rectiligne à la circulaire. Cette méthode inédite de fabrication de matériaux transparents possédant un très grand pouvoir rotatoire a permis de confirmer, pour la première fois, les nombreuses études théoriques antérieures et ouvre un champs d’applications pour ces guides d’ondes planaires propageant des modes non linéaires.
Elliptically polarized light cannot propagate in conventional planar waveguides. Indeed, because of their geometry, the propagated modes are restricted to linear polarizations, the famous TE/TM. One way to remove this restriction is the use of "chirOptical" waveguides. Thanks to the chirality of the material constituting the core of these guides and the refractive index difference between the core and the cladding layers, elliptical and even circular polarization modes can be propagated. The authors have demonstrated, for the first time, the propagation of nonlinear polarized light in planar waveguides. The core of these waveguides consists of a transparent chiral thin layer made from chiral hybrid silica with a high rotational power (2◦ / mm at 633nm). By a control of the refractive index contrast Δn between the layers, within 10-3, the polarization of the eigen modes have been modulated from linear to circular. This unprecedented fabrication method of transparent materials with a very high rotatory power allowed the confirmation, for the first time, of the many previous theoretical studies and opens a new field of applications of these planar waveguides propagating nonlinear modes.
24/11/2017